relative permeability measurement|relative permeability chart : importers Three Phase Relative Permeability: Methods of Relative Permeability Measurements. Unsteady state is the quickest method of obtaining relative permeability. In this method, the in-situ fluids are displaced at a constant rate with the effluent volumes being monitored continuously. 16 de jun. de 2023 · A partir de 19 de junho de 2023, a Invento Produções Inovadoras abre as portas do novo Trust Brasília. Como não poderia ser diferente, a 4ª edição do .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBAgitador brastemp 6kg. economiza frete Em carrinhos de compras. Ordenar por. Mais relevantes. Agitador Lavadora Brastemp Ative 11kg Bwl11 Bwb11 Original. por Batoni. .
Three Phase Relative Permeability: Methods of Relative Permeability Measurements. Unsteady state is the quickest method of obtaining relative permeability. In this method, the in-situ fluids are displaced at a constant rate with the effluent volumes being monitored continuously.Laboratory Measurements of Relative Permeability. There are essentially five .Laboratory Measurements of Relative Permeability. There are essentially five means by which relative permeability data can be obtained: Direct measurement in the laboratory by a steady . Relative-permeability data are essential for almost all calculations of fluid flow in hydrocarbon reservoirs. The data are used in making engineering estimates of productivity, .
Relative permeability has a first-order dependency on saturation level. However, many interstitial fluid distributions are possible for each level of saturation, depending on the direction of.By definition, the relative permeability is the ratio of the permeability of the phase at a given saturation level to the intrinsic permeability of the GDL at a given porosity. The relative .
Permeability is a measure of the abtily of porous materials to conduct flow and is,dictated by the geometry of the pore network. Generally, the fluid flow in hydrocarbon reservoirs involves . Relative permeability and capillary pressure defines relative permeabilities as dimensionless functions of saturation with values generally ranging between 0 and 1. Relative permeability is important for estimating the . Reservoir engineers use relative permeability and capillary pressure relationships for estimating the amount of oil and gas in a reservoir and for predicting the capacity for flow of .In multiphase flow in porous media, the relative permeability of a phase is a dimensionless measure of the effective permeability of that phase. It is the ratio of the effective .
A direct comparison between the relative permeability curves of well-characterized vugular porous media and their porous matrix showed that the incorporation of vugs leads to (i) higher equivalent absolute permeability, especially with longer cavities and higher vug density, (ii) increased oil occupancy in the porous matrix, due to less .Fundamentals of Fluid Flow in Porous Media Chapter 2 Permeability: Measurement of Permeability The permeability of a porous medium can be determined from the samples extracted from the formation or by in place .Fundamentals of Fluid Flow in Porous Media Chapter 2 Relative Permeability Laboratory Measurements of Relative Permeability: Steady State Techniques Steady-State techniques of estimating relative permeability are often . The “black-box method” is used to measure core samples in the laboratory [14].Many factors (e.g., tortuosity, characteristic scale, wettability) are combined and the flow conditions over time are measured using statistical methods [15], [16].It is difficult to control for one variable in this method, therefore studying the specific factors of relative permeability .
One-dimensional displacements are preferred for measurement of relative permeabilities. Nomenclature. C = parameter in the Land function k = permeability, L 2, md N c = capillary number S g = saturation of gas . R.F. 1995. Relative Permeability Hysteresis: Laboratory Measurements and a Conceptual Model. SPE Res Eng 10 (3): 222–228. SPE .
relative permeability model
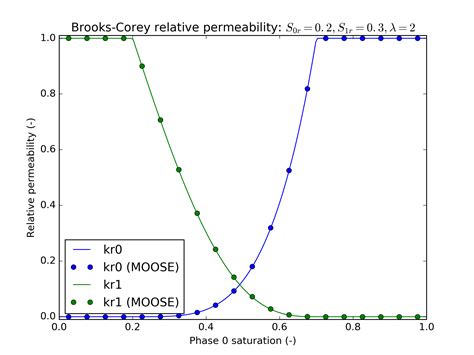
relative permeability lab measurements
The need for accurate measurement of capillary pressure and relative permeability functions increases with the resolution of reservoir models. With low-resolution models, there is a need for algorithms to "upscale" permeabilities, relative permeabilities, and capillary pressures from the scale of measurement on a small sample of rock to the . Using the conventional volumetric method in unsteady-state relative permeability measurements for unconventional gas reservoirs, such as coal and gas shale, is a significant challenge because the movable water volume in coal or shale is too small to be detected. Moreover, the dead volume in the measurement system adds extra inaccuracy to the .

Traditionally, steady-state relative permeability is calculated from measurements on small rock samples using Darcy’s law and assuming a homogenous saturation profile and constant capillary pressure. However, these assumptions are rarely correct as local inhomogeneities exist; furthermore, the wetting phase tends to be retained at the outlet–the so .
This phenomenon is called hysteresis. Fig. 1 shows a typical plot of two-phase relative permeability vs. saturation. It is ASOhelpful to present such plots on a semilog scale to expand the relative-permeability characteristics nea the endpoint saturation. Relative-permeability data are essential for almost all calculations of fluid flow in .RelativePermeabilityMeasurementsforMetal-Detector Research MichaelD.JanezicandJamesBaker-Jarvis ElectromagneticsDivision,NationalInstituteofStandardsandTechnology . Relative permeability is a dimensionless ratio that reflects the capability of oil, water, or gas to move through a formation compared with that of a single-phase fluid, commonly water. If a single fluid moves through rock, its relative permeability is 1.0. . has discussed the theory of transient permeability measurements, and the development .
A porous medium saturated with different fluids has different effective permeability to each one fluid. Relative permeability to one phase is the dimensionless measure of the effective permeability to that phase in multiphase flow in a porous medium (Mandal, 2007).For any one phase, the relative permeability is evaluated by dividing the effective permeability .Fundamentals of Fluid Flow in Porous Media Chapter 2 Relative Permeability Relative Permeability Curves When a wetting and a non-wetting phase flow together in a reservoir rock, each phase follows separate and distinct paths. The distribution of the two phases according to their wetting characteristics results in characteristic wetting and non-wetting phase relative . Relative permeability measurements can be obtained from either steady or unsteady-state tests. The best and most reliable data may be obtained from steady-state experiments from direct and accurate measurements with a whole coverage of the saturation interval (i.e., from interstitial water saturation to residual oil saturation). .
The resulting relative permeability curves from this set of repeatability experiments are plotted in Fig. iii, Fig. iv. The sets of relative permeability curves acquired before and after cleaning the sample were very similar, and provided strong confidence in the reliability and reproducibility of data acquisition methods used in this work.Another issue is that the measurement of relative permeability needs to be improved to obtain more accurate results, especially for through-plane relative permeability. In recent years, experimentally determined properties of the GDL, including capillary pressure relationships and water relative permeability have been employed in modeling works . The equipment required to measure relative permeability in SS is more complex than for USS measurements. The SS technique requires the capability to inject and measure fixed fractional flow of oil and water (or water and gas, or gas and oil) at low rates, and the resultant saturation changes. Pressure response is also determined at each .
Here are a few relative permeability values for different materials: Non-magnetic: Wood, plastic, glass, and most non-metallic substances have relative magnetic permeability values close to 1. They are generally considered to be non-magnetic. Wood: 1.00000043: Sapphire: 0.99999976: Relative permeability (k r) data are the key factors for describing the behaviour of the multi-phase flow in porous media.During the k r measurements of low-permeability rocks, high capillary pressure can cause a significant liquid hold-up at the core outlet. This liquid hold-up, which is known as capillary end effect (CEE), is the main difficulty for laboratory . Relative permeability, k r, w (S w), conveys the reduction in effective permeability of the wetting phase relative to the absolute permeability in the presence of the non-wetting phase [15] Relative permeability and capillary pressure of the hydrogen-water system in subsurface reservoirs was first investigated by Yekta et al. 2018 [ 16 ].Step 2: Deterimne λ by Plotting LogP c vs. LogS w *. Recall eq.(2‑130), Slope of the graph is –1/ λ = -1.25, Therefore, λ = 0.8 Step 4: Calculating Non-Wetting Phase Relative Permeability at Irreducible Wetting Phase Saturation ( k ro), Recall eq. (2‑129), k r o = 0.919 and S m = 0.95 = 1-S rg. Step 5: Calculating Relative Perm Values, Recall equations (2‑126) and (2‑127) to find .
Measurements of relative permeabilities indicated strong phase interference, with relative permeabilities reduced to very small values at intermediate saturations for both wetting and nonwetting phases. . These results run counter to a conventional view of fracture relative permeabilities that assumes that the relative permeability of each .
Relative permeability plays a crucial role in understanding the characteristics of gas and water seepage in porous media and in establishing production schedules in practical engineering applications. However, accurately determining water saturation in the relative permeability measurement is challenging due to the minimal detectable amount of movable .The Permeability of Free Space. The permeability of free space µ 0 (the permeability constant or the magnetic constant) is. µ 0 = 4π 10 -7 (H/m) ≈ 1.257 10-6 (H/m, N/A 2) The Relative Permeability. The relative permeability is the ratio of the permeability of a specific medium to the permeability of free space µ 0. µ r = µ / µ 0 (1) where To track the dynamic development of relative permeability measurements in the laboratory, discover the deficiencies, and discuss further work in this field, this paper investigates the relative . The most accurate manner to measure relative permeability is widely considered to be the steady-state method [13]. Here a sequence of fractional flows, f w, are applied: the pressure differential due to flow is recorded and the saturation measured from either mass balance or imaging. Typically, the relative permeability is measured on a .
We apply this technique to an induced fracture in a cylindrical basalt core undergoing water drainage. We find that the sum of the water and gas relative permeabilities is much <1 at intermediate saturations and the water relative permeability shows a sharp change over a narrow range of average water saturation.
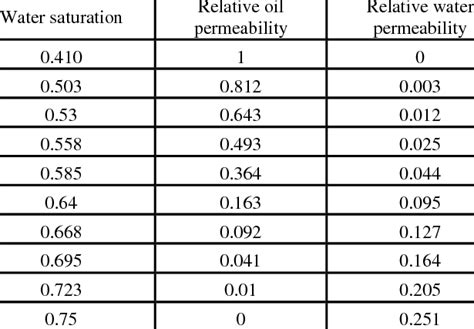
relative permeability chart
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät wand ausleihen
web52 linhas · Wii64 also exists as Cube64, a version of the emulator with the same UI and features albeit with tighter memory restrictions and less CPU power. This version has .
relative permeability measurement|relative permeability chart